Ovarian cancer begins in the ovaries. Ovaries are about the size of an almond. It produces hormones such as progesterone and estrogen, as well as eggs (ova).
In early-stage ovarian cancer, when the disease is confined to the ovary, it can be treated successfully. If it has spread over the abdomen and pelvis, it is quite difficult to treat ovarian cancer at such a stage.
According to a study, the regular use of talcum powder in the genital region directly or in the form of diaphragms, sanitary napkins, condoms, etc. increases the risk of getting ovarian cancer by 33%. The particles of the talcum powder cause ovarian cancer by traveling through the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes.
As a result, thousands of victims have filed talcum powder lawsuits against manufacturers such as J&J company.
Table of Contents
Formulating A Treatment Plan For Ovarian Cancer
There are various ways to treat ovarian cancer. It may include surgery, targeted treatments, hormone therapy, radiation, clinical trials, chemotherapy, and a combination of two or more therapies.
Factors Which Influence The Process Of Treatment Are:
- Age factors
- Stage of ovarian cancer at diagnosis
- The specific type of ovarian cancer
- Whether you plan to have children
- Whether you’re pre or postmenopausal
- Medical history
- Allergy to a particular kind of drug, etc.
Here, we discuss various chemotherapy treatments for ovarian cancer.
Chemotherapy For Ovarian Cancer
In chemotherapy, a combination of various powerful drugs injects in your body to treat ovarian cancer. It is a type of systemic treatment to seek and destroy cancer cells.

The platinum-based drug includes a combination of cisplatin or carboplatin (Paraplatin) with taxanes such as docetaxel (Taxotere) or paclitaxel (Taxol).
These drugs can be injected directly into your abdomen or given intravenously (IV) or orally. It’s used before and after the surgery to shrink tumors and kill any remaining cancer cells, respectively.
Chemotherapy For Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
Epithelial ovarian cancer begins in the cells on the outer lining of the ovaries. Chemotherapy treatment usually requires at least two IV drugs- three to six times, and three to four weeks apart.
The usual drug combination for such treatment involves carboplatin or cisplatin with docetaxel (Taxotere) or paclitaxel (Taxol).
Chemotherapy For Ovarian Cancer That Begins In Germ Cells
Ovarian germ cell tumor is a disease in which cancer develops in the germ (egg) cells of the ovary. It usually occurs in teenage girls or young women and mostly affects only one ovary. In some extreme cases, both the ovaries got affected by germ cell tumors.
The drug combination used for chemotherapy involves bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin (Platinol).
Chemotherapy For Ovarian Cancer That Begins In Stromal Cells
Ovarian stromal cancer is one of the rare kinds of cancer that begins in the connective tissue cells that help ovary to release progesterone, estrogen, and other female hormones.
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors and granulosa-theca tumors are the most common type of Ovarian stromal cancer. This drug combination for treating ovarian stromal cancer is similar to the treatment for germ cell tumors.
Other Approved Chemotherapy Treatments
There are various chemotherapies available for ovarian cancer. Some of them are:
- Vinorelbine (Navelbine)
- Albumin-bound Paclitaxel (Abraxane)
- Vinblastine (Velban)
- Altretamine (Hexalen)
- Topotecan (Hycamtin)
- Capecitabine (Xeloda)
- Pemetrexed (Alimta)
- Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan)
- Melphalan (Alkeran)
- Gemcitabine (Gemzar)
- Liposomal Doxorubicin (Doxil)
- Ifosfamide (Ifex)
- Irinotecan (Camptosar)
Side Effects Of Chemotherapy
Side effects may vary depending on the drug combination and the stage of ovarian cancer. The common side effects may include:
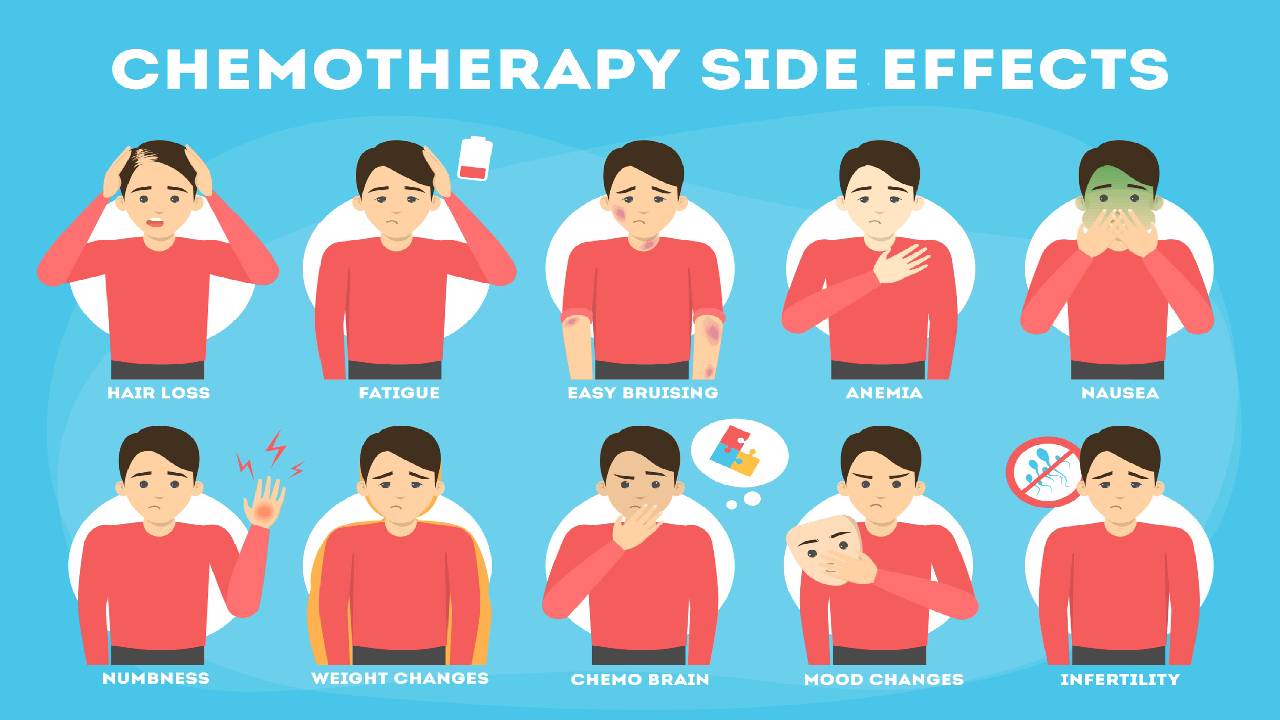
- Infection
- Hair loss
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Constipation
- Fertility problems
- Changes in appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weight gain or weight loss
- Easy bruising and bleeding
- Anemia (low red blood cell counts)
- Changes in libido and sexual function
- Urine and bladder changes and kidney problems
- Chemo brain, which can affect concentration and focus
- Nerve and muscle problems- pain, tingling, and numbness
- Mouth, tongue, and throat problems including pain with swallowing
Some of these side effects are temporary. If you are experiencing it for a long time, consult your doctor. There are some other serious and long-lasting side effects, such as kidney damage, early menopause, etc.
Conclusion
The primary goal of chemotherapy treatment before the surgery is to shrink the tumor so that it can be easy to remove.
After the surgery, chemotherapy is used to destroy any cancer cells remaining in the patient’s body. The chemotherapy treatment typically begins when the patient is considered healthy enough to withstand its side effects.